-

-
全部+
Java技术
- POI教程
- EJB教程
- JSP教程
- ANT教程
- ibatis教程
- hibernate教程
- JDBC教程
- JasperReports教程
- java实例教程
- Java.math包教程
- MyBatis教程
- Spring教程
- JavaMail教程
- TestNG教程
- AWT教程
- jMeter教程
- Swing教程
- Java.util包教程
- Struts2教程
- Maven教程
- Java.io包教程
- Lucene教程
- JFreeChart教程
- JPA教程
- EasyMock教程
- Guava教程
- JavaFX教程
- SpringMVC教程
- Shiro教程
- Tika教程
Web开发
Web开发
- jQuery教程
- AngularJS教程
- VBScript教程
- Javascript教程
- CSS教程
- Ruby On Rails教程
- HTTP协议教程
- XHTML教程
- HTML5教程
- HTML教程
- ASP.NET教程
- JSF教程
- GWT教程
- Flex教程
- Uploadify教程
框架
- Java
- MySQL
- 最新文章
-

一个if语句后面可以跟一个可选的else语句,该语句执行时的布尔表达式为false。
语法
在D编程语言的if... else语句的语法是:
if(boolean_expression)
{
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true */
}
else
{
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is false */
}
如果布尔表达式的值为true,那么if代码块将被执行代码,否则else块将被执行。
D编程语言假设任何非零和非空值作为true,如果是零或null,则假定为false。
流程图:
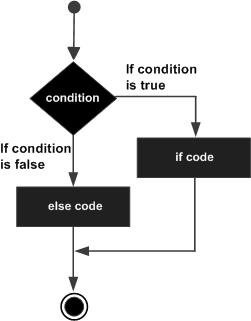
例子:
import std.stdio;
int main ()
{
/* local variable definition */
int a = 100;
/* check the boolean condition */
if( a < 20 )
{
/* if condition is true then print the following */
writefln("a is less than 20" );
}
else
{
/* if condition is false then print the following */
writefln("a is not less than 20" );
}
writefln("value of a is : %d", a);
return 0;
}
当上面的代码被编译并执行,它会产生以下结果:
a is not less than 20; value of a is : 100
if...else if...else语句
一个if后面可以跟一个可选的if... else语句,如果测试各种条件下... else if语句,可使用单一的else语句。
当使用 if , else if , else语句有几点要记住:
-
if可以有零个或else,它必须跟在else if后面。
-
if 可以有零到多个else if,它们必须在else之前。
-
一旦一个 else if 匹配成功,剩余else if不会被测试或计算。
语法
if...else if...else语句在D编程语言的语法是:
if(boolean_expression 1)
{
/* Executes when the boolean expression 1 is true */
}
else if( boolean_expression 2)
{
/* Executes when the boolean expression 2 is true */
}
else if( boolean_expression 3)
{
/* Executes when the boolean expression 3 is true */
}
else
{
/* executes when the none of the above condition is true */
}
例子:
import std.stdio;
int main ()
{
/* local variable definition */
int a = 100;
/* check the boolean condition */
if( a == 10 )
{
/* if condition is true then print the following */
writefln("Value of a is 10" );
}
else if( a == 20 )
{
/* if else if condition is true */
writefln("Value of a is 20" );
}
else if( a == 30 )
{
/* if else if condition is true */
writefln("Value of a is 30" );
}
else
{
/* if none of the conditions is true */
writefln("None of the values is matching" );
}
writefln("Exact value of a is: %d", a );
return 0;
}
当上面的代码被编译并执行,它会产生以下结果:
None of the values is matching Exact value of a is: 100

