switch语句允许根据值列表测试变量的相等性。 每个值被称为一个情况(case),并且对于每个开关情况(switch case)检查接通的变量。
在Go编程中,switch有两种类型。
- 表达式开关(switch) - 在表达式开关(switch)中,case包含与开关(switch)表达式的值进行比较的表达式。
- 类型开关(switch) - 在类型开关(switch)中,case包含与特殊注释的开关(switch)表达式的类型进行比较的类型。
表达式开关(switch)
Go编程语言中的表达式switch语句的语法如下:
switch(boolean-expression or integral type){
case boolean-expression or integral type :
statement(s);
case boolean-expression or integral type :
statement(s);
/* you can have any number of case statements */
default : /* Optional */
statement(s);
}
以下规则适用于switch语句:
-
在switch语句中使用的表达式必须具有整数或布尔表达式, 或者是一个具有单个转换函数为整数或布尔值的类类型。如果未传递表达式,则默认值为true。
-
在switch语句中可以有任意数量的case语句。 每个case后面都跟要比较的值和冒号。
- case的常量表达式必须是与switch语句的变量是相同的数据类型,并且它必须是常量或文字。
- 当被打开的变量等于一个case中的值,那么将执行case之后的语句。在case语句中可不需要break语句。
- switch语句可有一个可选的default,它必须出现在switch语句的末尾。default可用于在没有任何case为真时执行任务。default之后可不需要break语句。
流程图
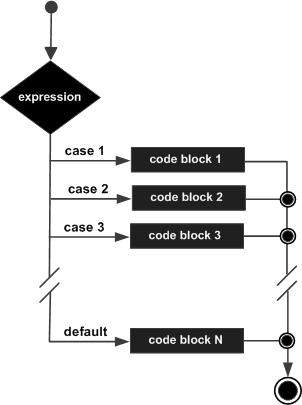
示例
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
/* local variable definition */
var grade string = "B"
var marks int = 90
switch marks {
case 90: grade = "A"
case 80: grade = "B"
case 50,60,70 : grade = "C"
default: grade = "D"
}
switch {
case grade == "A" :
fmt.Printf("Excellent!\n" )
case grade == "B", grade == "C" :
fmt.Printf("Well done\n" )
case grade == "D" :
fmt.Printf("You passed\n" )
case grade == "F":
fmt.Printf("Better try again\n" )
default:
fmt.Printf("Invalid grade\n" );
}
fmt.Printf("Your grade is %s\n", grade );
}
当上述代码编译和执行时,它产生以下结果:
Excellent! Your grade is A
类型开关(switch)
Go编程语言中的类型switch语句的语法如下:
switch x.(type){
case type:
statement(s);
case type:
statement(s);
/* you can have any number of case statements */
default: /* Optional */
statement(s);
}
以下规则适用于switch语句:
- switch语句中使用的表达式必须具有接口{}类型的变量。
- 在switch中可以有任意数量的case语句。 每个case后面都跟要比较的值和冒号。
- case语句的类型必须与switch语句中的变量具有相同的数据类型,并且必须是有效的数据类型。
- 当switch中的变量等于一个case语句中的值,那么case之后的语句将被执行。在case语句中可不需要break。
- switch语句可以具有可选的default,它必须出现在switch语句的末尾。default情况可用于在没有任何case语句为真时执行任务。在default不需要break语句。
示例
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x interface{}
switch i := x.(type) {
case nil:
fmt.Printf("type of x :%T",i)
case int:
fmt.Printf("x is int")
case float64:
fmt.Printf("x is float64")
case func(int) float64:
fmt.Printf("x is func(int)")
case bool, string:
fmt.Printf("x is bool or string")
default:
fmt.Printf("don't know the type")
}
}
当上述代码编译和执行时,它产生以下结果:
type of x :<nil>
我要分享文章
最近发布 »
- windows IIS6服务器全站301永久重定向设置方法
- thinkPHP实现签到功能的方法
- 详解java代码中init method和destroy method的三种使用方式
- Python获取文件所在目录和文件名的方法
- linux sudo命令详解
- 用于判断用户注册时,密码强度的JS代码
- Django-Rest-Framework 权限管理源码浅析(小结)
- 服务器 安全检查要点[星外提供]
- python 导入数据及作图的实现
- JS正则替换去空格的方法
- 微信小程序promsie.all和promise顺序执行
- Android实现渐变色的圆弧虚线效果
- Python中文编码那些事
- JS跨域请求外部服务器的资源
- asp的程序能实现伪静态化的方法
- 基于Vue.js与WordPress Rest API构建单页应用详解
- 修改MaxFieldLength与MaxRequestBytes彻底解决Request Too Long的问题
- sql字符串函数大全和使用方法示例


