C++实现动态顺序表
时间:2020-10-05 21:34:29 | 栏目:C代码 | 点击:次
本文实例为大家分享了C++实现动态顺序表的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
Vector.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int DataType;
class Vector
{
public:
Vector()
:_first(NULL)
, _finish(NULL)
, _endofstorage(NULL)
{}
Vector(const Vector& v)
{
if (v.Size() > 0)
{
_first = new DataType[v.Size()]; //只开辟原有数据所占空间大小,节省空间
memcpy(_first, v._first, sizeof(DataType)*v.Size());
if (_first)
{
_finish = _first + v.Size();
_endofstorage = _first + v.Size();
}
else
{
_first = _finish = _endofstorage = NULL;
}
}
}
Vector& operator=(Vector& v)
{
if (this != &v)
{
////传统写法
//DataType* tmp = new DataType[v.Size()];
//memcpy(tmp, _first, sizeof(DataType)*v.Size());
//delete[] _first;
//_first = tmp;
//_finish = _first + v.Size();
//_endofstorage = _first + v.Size();
//现代写法
swap(_first, v._first);
swap(_finish, v._finish);
swap(_endofstorage, v._endofstorage);
}
return *this;
}
~Vector()
{
delete[] _first;
_first = _finish = _endofstorage = NULL;
}
void Print()
{
DataType* cur = _first;
while (cur != _finish)
{
cout << *cur << " ";
++cur;
}
cout << endl;
}
size_t Size() const;
size_t Capacity() const;
void Expand(size_t n);
void PushBack(DataType x);
void Reserve(size_t n);
void PopBack();
void Insert(size_t pos, DataType x);
void Erase(size_t pos);
size_t Find(DataType x);
private:
DataType* _first;
DataType* _finish;
DataType* _endofstorage;
};
size_t Vector::Size() const
{
return _finish - _first;
}
size_t Vector::Capacity() const
{
return _endofstorage - _first;
}
void Vector::Expand(size_t n)
{
if (n > Capacity())
{
size_t size = Size();
DataType* tmp = new DataType[n];
memcpy(tmp, _first, sizeof(DataType)*size);
delete[] _first;
_first = tmp;
_finish = _first + size; //切记更新新的_finish和_endofstorage
_endofstorage = _first + n;
}
}
void Vector::PushBack(DataType x)
{
//if (_finish == _endofstorage)
//{
// if (Capacity() == 0)
// {
// Expand(3);
// }
// else
// {
// Expand(Capacity() * 2);
// }
//}
//*_finish = x;
//++_finish;
Insert(Size(), x);
}
void Vector::Reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > Capacity())
{
Expand(n);
}
}
void Vector::PopBack()
{
assert(_finish > _first);
--_finish;
}
void Vector::Insert(size_t pos, DataType x)
{
assert(pos <= Size());
if (_finish == _endofstorage)
{
if (Capacity() == 0)
{
Expand(3);
}
else
{
Expand(Capacity() * 2);
}
}
int end = Size() - 1;
while (end >= (int)pos)
{
_first[end + 1] = _first[end];
--end;
}
_first[pos] = x;
++_finish;
}
void Vector::Erase(size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < Size());
size_t cur = pos;
while (cur < Size() - 1)
{
_first[cur] = _first[cur + 1];
++cur;
}
--_finish;
}
size_t Vector::Find(DataType x)
{
DataType* cur = _first;
while (cur != _finish)
{
if (*cur == x)
{
return cur - _first;
}
++cur;
}
return -1;
}
void TestVector()
{
Vector v1;
v1.PushBack(1);
v1.PushBack(2);
v1.PushBack(3);
v1.PushBack(4);
v1.Print();
size_t pos = v1.Find(2);
printf("pos expect 1,actual %lu\n", pos);
Vector v2(v1);
v2.Insert(0, 0);
v2.Print();
Vector v3;
v3 = v2;
v3.Print();
v3.Erase(1);
v3.Print();
}
test.cpp
#include "Vector.h"
int main()
{
cout << "顺序表:" << endl;
TestVector();
return 0;
}
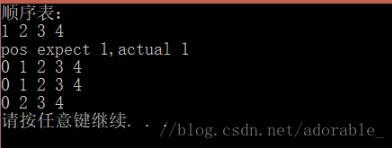
效果: